

Paynter RW (2002) Surf Interface Anal 33:14–22 Paynter RW (2004) J Electron Spectrosc Relat Phenom 135:183–190 Haïdopoulos M, Horgnies M, Mirabella F, Pireaux JJ (2008) Plasma Processes Polym 5:67–75 Shi MK, Martinu L, Sacher E, Selmani A, Wertheimer MR, Yelon A (1995) Surf Interface Anal 23:99–104 Parry KL, Shard AG, Short RD, White RG, Whittle JD, Wright A (2006) Surf Interface Anal 38:1497–1504 Paynter RW (1999) Surf Interface Anal 27:103–113īutoi CI, Mackie NM, Gamble LJ, Castner DG, Barnd J, Miller AM, Fisher ER (2000) Chem Mater 12:2014–2024 Powell CJ, Jablonski A (2000) Surf Interface Anal 29:108–114

Girard-Lauriault PL, Mwale F, Iordanova M, Demers C, Desjardins P, Wertheimer MR (2005) Plasma Processes Polym 2:263–270įavia P, d’Agostino R (1998) Surf Coat Technol 98:1102–1106īrady RF Jr (2004) Comprehensive desk reference of polymer characterization and analysis. Siow KS, Britcher L, Kumar S, Griesser HJ (2006) Plasma Processes Polym 3:392–418 Our conclusions are supported by simulations using SESSA software.įoerch R, Chifen AN, Bousquet A, Khor HL, Jungblut M, Chu L-Q, Zhang Z, Osey-Mensah I, Sinner E-K, Knoll W (2007) Chem Vap Depos 13:280–294 Results show that while laboratory XPS, and even ARXPS, suggest homogenous surface chemistries, the novel combination of ARXPS and ERXPS points to the existence of a compositional profile in the extreme outer surface layer. The surface-near chemistry is investigated using both high-resolution C 1s spectra and elemental concentrations derived from elemental peak intensities. Using a combination of both techniques, z 95% can be varied continuously from 0.7 to 11 nm.
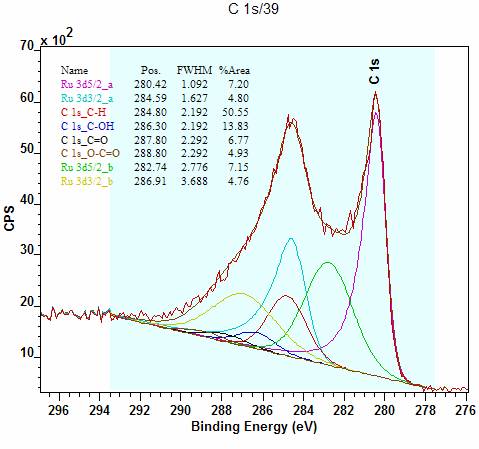
These two techniques enable one to tune the “XPS 95%” information depth, z 95%, by varying either the angle or the excitation energy. These films were investigated using angle-resolved and excitation energy resolved X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (ARXPS and ERXPS, respectively) in order to determine their sub-surface chemical profiles. Nitrogen (N)-rich organic thin films were deposited using both low-pressure plasma- and vacuum-ultraviolet-based techniques, from mixtures of ammonia (NH 3) and ethylene (C 2H 4).


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
